Setting Up ntopng On My Home Network To Monitor Internet Traffic
Contents
Goal
Monitor network traffic to and from the internet via my cable modem so that I can stay under my data cap.
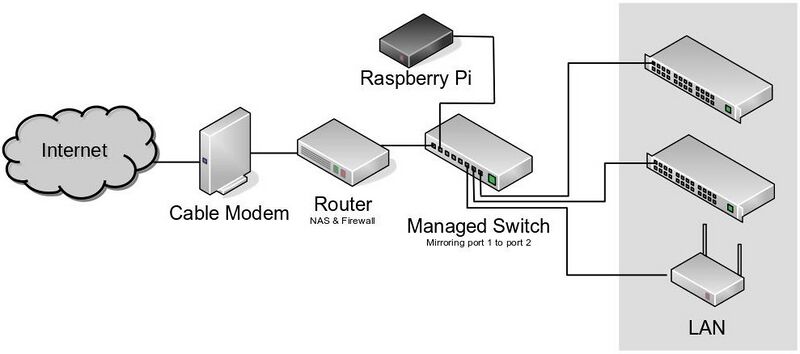
Architectural Overview
- The "Managed Switch" connects all of the various components of my local LAN together with the "Router" that is my gateway to the internet.
- The "Managed Switch" is configured to mirror all of the packets on the port that the "Router" is plugged into over to the port that the "Raspberry Pi" is plugged into.
- The Raspberry Pi runs the "ntopng" application to collect and analyze the netflow data. It provides a web GUI at port 3000 on my LAN.
Setup The Raspberry Pi
Install Raspian on the Pi. As of this writing that is the "Buster" version of Raspian.
Install mariadb-server and redis database packages.
Run mysql_secure_installation
Set up ntop MySQL database:
# mysql -u root -p Enter password: Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. mysql> create database ntopng; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> CREATE USER 'ntopng'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Yoursecretpassword'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ntopng . * TO 'ntopng'@'localhost'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Install GeoIP databases
Install the geoipupdate armv6 binary from the Maxmind releases page on github: https://github.com/maxmind/geoipupdate/releases.
Create an account at MaxMind, register for an API key, and edit /usr/local/etc/GeoIP.conf as follows:
# GeoIP.conf file for `geoipupdate` program, for versions >= 3.1.1. # Used to update GeoIP databases from https://www.maxmind.com. # For more information about this config file, visit the docs at # https://dev.maxmind.com/geoip/geoipupdate/. # `AccountID` is from your MaxMind account. AccountID YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID_HERE # `LicenseKey` is from your MaxMind account. LicenseKey YOUR_LICENSE_KEY_HERE # `EditionIDs` is from your MaxMind account. EditionIDs GeoLite2-ASN GeoLite2-City GeoLite2-Country # The directory to store the database files. Defaults to /usr/local/share/GeoIP DatabaseDirectory /usr/share/GeoIP
Run sudo mkdir /usr/share/GeoIP to create the target directory.
Run sudo geoipupdate command to install the GeoIP database files.
Compile and install the nDPI and ntopng packages from github.com/ntop
Prepare the development environment
$ sudo apt install autoconf libtool libjson-c-dev libpcap-dev libgcrypt20-dev autogen autogen-doc bison flex guile-2.0-libs libbison-dev libfl-dev libgc1c2 libnuma-dev libopts25 libopts25-dev libpcre2-32-0 libpcre2-dev libtool-bin libssl-dev librrd-dev libcurl4-openssl-dev libmaxminddb-dev libsqlite3-dev libxml2-dev rrdtool libhiredis-dev libpango1.0-dev libcairo2-dev libnetfilter-queue-dev libcap-dev libnetfilter-conntrack-dev libreadline-dev libldap2-dev rename libsnmp-dev libzmq3-dev default-libmysqlclient-dev
Compiling nDPI
$ cd ~/src $ git clone https://github.com/ntop/nDPI.git $ cd nDPI $ ./autogen.sh $ ./configure $ make -j 4 $ sudo make install
Compiling ntopng
$ cd .. $ git clone https://github.com/ntop/ntopng.git $ cd ntopng I had to modify Makefile.in before compiling ntopng, see below $ ./autogen.sh $ ./configure $ make -j 4 $ sudo make install
Patching ntopng
There were libraries missing from the linking step in the compile process for ntopng. I modified the Makefile.in file as follows to include them:
--- Makefile.in.orig 2020-12-14 14:49:45.264274622 -0500
+++ Makefile.in 2020-12-14 14:41:01.671021439 -0500
@@ -17,6 +17,10 @@
GET_UTIL = wget --no-proxy -nc
endif
+###### dlk added
+DLK_LIBS = -latomic -lgpg-error
+######
+
######
NDPI_LIB = @NDPI_LIB@
NDPI_INC = @NDPI_INC@
@@ -106,7 +110,7 @@
######
TARGET = ntopng
-NLIBS = $(NDPI_LIB) $(LIBPCAP) $(LUA_LIB) $(LIBRRDTOOL_LIB) $(ZEROMQ_LIB) $(JSON_LIB) $(SNMP_LIB) @MAXMINDDB_LIB@ $(SODIUM_LIB) @HIREDIS_LIB@ @SQLITE_LIB@ @MYSQL_LIB@ @RADCLI_LIB@ @EXPAT_LIB@ @SSL_LIB@ @LINK_OPTS@ @LDFLAGS@ @PRO_LIBS@ $(ZSTD_LIB) -lm -lpthread
+NLIBS = $(DLK_LIBS) $(NDPI_LIB) $(LIBPCAP) $(LUA_LIB) $(LIBRRDTOOL_LIB) $(ZEROMQ_LIB) $(JSON_LIB) $(SNMP_LIB) @MAXMINDDB_LIB@ $(SODIUM_LIB) @HIREDIS_LIB@ @SQLITE_LIB@ @MYSQL_LIB@ @RADCLI_LIB@ @EXPAT_LIB@ @SSL_LIB@ @LINK_OPTS@ @LDFLAGS@ @PRO_LIBS@ $(ZSTD_LIB) -lm -lpthread
CPPFLAGS = @CFLAGS@ @HIREDIS_INC@ $(MONGOOSE_INC) $(JSON_INC) $(SNMP_INC) $(SODIUM_INC) $(NDPI_INC) $(LUA_INC) $(LIBRRDTOOL_INC) $(ZEROMQ_INC) @MYSQL_INC@ @CPPFLAGS@ -I$(HTTPCLIENT_INC) @SSL_INC@ @PRO_INCS@ -DDATA_DIR='"$(datadir)"' -I${PWD}/third-party/libgeohash -I${PWD}/third-party/patricia # -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG
######
# ntopng-1.0_1234.x86_64.rpm
Starting ntopng
Create /etc/ntopng/ntopng.conf, setting the interface to match the actual name of the network interface and dump-flows to match the MySQL database and userid you set up.
# The configuration file is similar to the command line, with the exception that an equal # sign '=' must be used between key and value. Example: -i=p1p2 or --interface=p1p2 For # options with no value (e.g. -v) the equal is also necessary. Example: "-v=" must be used. # # # -G|--pid-path # Specifies the path where the PID (process ID) is saved. This option is ignored when # ntopng is controlled with systemd (e.g., service ntopng start). # # -G=/var/run/ntopng.pid # # -e|--daemon # This parameter causes ntop to become a daemon, i.e. a task which runs in the background # without connection to a specific terminal. To use ntop other than as a casual monitoring # tool, you probably will want to use this option. This option is ignored when ntopng is # controlled with systemd (e.g., service ntopng start) # # -e= # # -i|--interface # Specifies the network interface or collector endpoint to be used by ntopng for network # monitoring. On Unix you can specify both the interface name (e.g. lo) or the numeric # interface id as shown by ntopng -h. On Windows you must use the interface number instead. # Note that you can specify -i multiple times in order to instruct ntopng to create multi- # ple interfaces. # # -i=eth1 # -i=eth2 -i=eth0 # # -w|--http-port # Sets the HTTP port of the embedded web server. # # -w=3000 # # -m|--local-networks # ntopng determines the ip addresses and netmasks for each active interface. Any traffic on # those networks is considered local. This parameter allows the user to define additional # networks and subnetworks whose traffic is also considered local in ntopng reports. All # other hosts are considered remote. If not specified the default is set to 192.168.1.0/24. # # Commas separate multiple network values. Both netmask and CIDR notation may be used, # even mixed together, for instance "131.114.21.0/24,10.0.0.0/255.0.0.0". # # -m=10.10.123.0/24 # -m=10.10.124.0/24 # # -n|--dns-mode # Sets the DNS address resolution mode: 0 - Decode DNS responses and resolve only local # (-m) numeric IPs 1 - Decode DNS responses and resolve all numeric IPs 2 - Decode DNS # responses and don't resolve numeric IPs 3 - Don't decode DNS responses and don't resolve # -n=1 # # -S|--sticky-hosts # ntopng periodically purges idle hosts. With this option you can modify this behaviour by # telling ntopng not to purge the hosts specified by -S. This parameter requires an argu- # ment that can be "all" (Keep all hosts in memory), "local" (Keep only local hosts), # "remote" (Keep only remote hosts), "none" (Flush hosts when idle). # # -S= # # -d|--data-dir # Specifies the data directory (it must be writable by the user that is executing ntopng). # # -d=/var/lib/ntopng # # -q|--disable-autologout # Disable web interface logout for inactivity. # # -q= # # -F|--dump-flows <mode> # If ntopng is compiled with sqlite support, flows can dumped persis‐ # tently on disk using this option. The mode can be set to es - Dump on # ntopng.es queue in Elasticsearch format that be insert on a ES data‐ # base. In this case the format is "es;<idx type>;<idx name>;<es # URL>;<http auth>". Example: -F "es;ntopng;ntopng-%Y.%m.%d;http://lo‐ # calhost:9200/_bulk;user:pwd". The <idx name> accepts the strftime() # format. mysql - Dump flows in MySQL tables. In this case the format # is "<host[@port]|unix socket>:<dbname>:<table>:<user>:<pw>". Example # -F "mysql;localhost;ntopng;flows-%Y.%m.%d;root;". # -F="mysql;localhost;ntopng;ntopng_table;ntopng;Yoursecretpassword"
Create /usr/lib/systemd/system/ntopng.service, setting the correct interface name in the ExecStartPre ethtool command:
[Unit] Description=ntopng high-speed web-based traffic monitoring and analysis tool After=mariadb.service redis.service Requires=mariadb.service redis.service Wants=network.target [Service] Type=simple ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/ethtool -K ens9 gro off gso off tso off ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/ntopng /etc/ntopng/ntopng.conf Restart=on-failure RestartSec=5 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Notes
Resetting ntopng password
$ sudo redis-cli del ntopng.user.admin.password
Restart ntopng
Password will revert to default: admin
Deleting ntopng data
$ sudo rm -fr /var/lib/ntopng $ mysql -u notopng -p ntopng > drop table flowsv4, flowsv6; > quit;
Can also delete data from redis, which will clear settings and passwords as well:
$ sudo redis-cli keys "ntopng.*" | xargs sudo redis-cli del $ sudo redis-cli keys "ntonpng.*" | xargs sudo redis-cli del
After deleting ntopng data as described above, the six category list files defined by default will not exist. Errors will appear in the console log to that effect. These tables can be loaded (updated) manually from the Category Lists menu in the UI or they will get updated automatically as ntopng runs.